Xét các số thực dương x y thỏa mãn log căn 3 dx + yx^2 + y^2 + xy + 2 = x( x - 3 ) + y( y - 3 ) +

Câu hỏi
Nhận biếtXét các số thực dương x, y thỏa mãn \({\log _{\sqrt 3 }}\dfrac{{x + y}}{{{x^2} + {y^2} + xy + 2}} = x\left( {x - 3} \right) + y\left( {y - 3} \right) + xy.\) Tìm giá trị \({P_{m{\rm{ax}}}}\) của biểu thức \(P = \dfrac{{5x + 4y + 4}}{{x + y + 3}}\).
Đáp án đúng: D
Lời giải của Tự Học 365
Giải chi tiết:
\(\begin{array}{l}{\log _{\sqrt 3 }}\frac{{x + y}}{{{x^2} + {y^2} + xy + 2}} = x\left( {x - 3} \right) + y\left( {y - 3} \right) + xy\,\,\,\,\,\,\left( 1 \right)\\ \Leftrightarrow {\log _{\sqrt 3 }}\left( {x + y} \right) - {\log _{\sqrt 3 }}\left( {{x^2} + {y^2} + xy + 2} \right) = {x^2} - 3x + {y^2} - 3y + xy\\ \Leftrightarrow {\log _{\sqrt 3 }}\left( {x + y} \right) + 3x + 3y = {\log _{\sqrt 3 }}\left( {{x^2} + {y^2} + xy + 2} \right) + {x^2} + {y^2} + xy\\ \Leftrightarrow {\log _{\sqrt 3 }}\left( {x + y} \right) + 2 + 3x + 3y = {\log _{\sqrt 3 }}\left( {{x^2} + {y^2} + xy + 2} \right) + {x^2} + {y^2} + xy + 2\\ \Leftrightarrow {\log _{\sqrt 3 }}\left( {3x + 3y} \right) + 3x + 3y = {\log _{\sqrt 3 }}\left( {{x^2} + {y^2} + xy + 2} \right) + {x^2} + {y^2} + xy + 2\,\,\,\,\,\,\left( 2 \right)\end{array}\)
Đặt \(f\left( t \right) = {\log _{\sqrt 3 }}t + t\,\,\,\left( {t > 0} \right) \Rightarrow f'\left( t \right) = \frac{1}{{t\ln \sqrt 3 }} + 1 > 0\,\,\forall t > 0 \Rightarrow f\left( t \right)\) đồng biến trên \(\left( {0; + \infty } \right)\)
\(\begin{array}{l}\left( 2 \right) \Leftrightarrow f\left( {3x + 3y} \right) = f\left( {{x^2} + {y^2} + xy + 2} \right) \Leftrightarrow 3x + 3y = {x^2} + {y^2} + xy + 2\\ \Leftrightarrow 4{x^2} + 4{y^2} + 4xy - 12x - 12y + 8 = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow {\left( {2x + y} \right)^2} - 6\left( {2x + y} \right) + 5 = - 3{\left( {y - 1} \right)^2} \le 0 \Leftrightarrow 1 \le 2x + y \le 5\end{array}\)
Khi đó, \(P = \frac{{5x + 4y + 4}}{{x + y + 3}} = 3 + \frac{{2x + y - 5}}{{x + y + 3}} \le 3\), vì \(\left\{ \begin{array}{l}2x + y - 5 \le 0\\x + y + 3 > 0\end{array} \right.\)
Vậy \({P_{m{\rm{ax}}}} = 3\) khi và chỉ khi \(\left\{ \begin{array}{l}2x + y - 5 = 0\\y - 1 = 0\end{array} \right. \Leftrightarrow \left\{ \begin{array}{l}x = 2\\y = 1\end{array} \right.\)
Chọn D.
Luyện tập
Câu hỏi liên quan
-







Trong không gian với hệ trục Oxyz, cho mặt phẳng (P): 2x + y + 2z + 4 = 0, đường thẳng d:
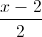 =
= 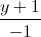 =
= 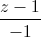 và đường thẳng ∆ là giao tuyến của hai mặt phẳng x = 1, y + z - 4 = 0. Viết phương trình mặt cầu có tâm thuộc d, đồng thời tiếp xúc với ∆ và (P) biết rằng tâm của mặt cầu có tọa độ nguyên.
và đường thẳng ∆ là giao tuyến của hai mặt phẳng x = 1, y + z - 4 = 0. Viết phương trình mặt cầu có tâm thuộc d, đồng thời tiếp xúc với ∆ và (P) biết rằng tâm của mặt cầu có tọa độ nguyên.

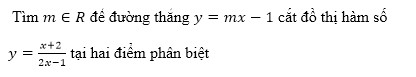
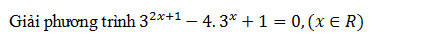

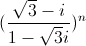 là số thực và z2 =
là số thực và z2 = 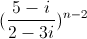 là số ảo.
là số ảo.